
The newly updated leads4pass 300-410 dumps contain 807 (2024 contain 877) exam questions and answers, as well as provide difficult analysis, in line with the Cisco 300-410 ENARSI certification exam conditions!
Because leads4pass 300-410 dumps are actually verified by a professional team, it is real and effective! And provide two learning types: 300-410 dumps PDF, and 300-410 dumps VCE, both types contain the latest 300-410 exam questions!
So, get the latest 300-410 dumps in PDF or VCE format from leads4pass: https://www.leads4pass.com/300-410.html, to ensure you pass the exam easily.
Updates all the time in 2024

We can’t keep using materials from the past to solve today’s problems!
Some people say that there is no difference between 300-410 ENARSI v1.0 and the current V1.1. This difference has changed since September 2023. If you have had experience in this area, you will definitely know the situation.
There really hasn’t been much change since September last year! Check out the previous 300-410 ENARSI exam materials to know the real difference, right? Any changes can be obtained through the new 300-410 ENARSI exam materials I shared today.
Share New 300-410 ENARSI Exam Materials
| From | Number of exam questions | Update | Type |
| Leads4Pass | 12/877 | 2024 | Free |
NEW QUESTION 1:
You have configured BGP on both rtrA in AS 1 and rtrB in AS 2. There are two routes created using the network command between the two routers. One route traverses through AS 5 and AS 6 from rtrA to rtrB, while the other route traverses AS 7, AS 8, and AS 9 from rtrA to rtrB. Both routes use default values for the Weight and LOCAL_PREF attributes.
Which of the following attributes determines the BEST route between rtrA and rtrB routers?
A. Weight
B. LOCAL_PREF
C. Origin type
D. AS_PATH
Correct Answer: D
The AS_PATH attribute is used to determine the best path between the two routes. To select the best path from rtrA to rtrB, BGP analyzes attributes that are set for the two available routes during the configuration of the network. The key BGP attributes and the order in which they are checked are as follows:
1.
Weight – the highest weight is selected
2.
LOCAL_PREF – highest LOCAL_PREF is selected
3.
Locally originated routes – local routes are selected
4.
AS_PATH – shortest AS_PATH is selected
5.
Origin type – lowest origin type is selected
6.
Multi-exit Discriminator (MED) – lowest MED is selected
The weight attribute is the first attribute to be checked while selecting the best BGP route. This attribute is relevant only to the local router on which it is set. The value of this attribute can be any number from 0 to 65535. The default values are 32768 for locally originated routes and 0 for other types of routes. Both routes in this case originated locally and have the default weight values. Therefore, in this case, the weight attribute is not used to determine the best route.
BGP then checks the value of the LOCAL_PREF attribute, which refers to local preference. Local preference is a value that indicates the route that is preferred to exit the AS to reach a given network. Routes with higher local preferences are selected by BGP. You can set the local preference for a route to any value; however, if you do not, the route uses the default value of 100. Because both routes have the default LOCAL_PREF value, this attribute is not used to determine the best route.
Next BGP checks whether any of the routes are locally originated using the network, redistribute, or aggregate commands. As stated, both routes originated using the network command on the routers. Consequently, BGP analyzes the value of the AS_PATH attribute, which is a list of the AS numbers traversed by a particular route.
The route with the shortest AS_PATH is selected as the best path. In this case, the route that consists of AS 5 and 6 is considered the best path because the AS_PATH value for this route is shorter than that for the route traversing AS 7, 8, and 9.
The AS_PATH value for the route traversing AS 5 and 6 is [6 5 1], while the AS_PATH for the route traversing AS 7, 8, and 9 is [9 8 7 1].
The other options are incorrect because the corresponding attributes are the same for both routes; hence, those attributes are not considered while BGP determines the best path.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Explain BGP attributes and best-path selection
References:
Internetworking Technology Handbook > BGP > BGP attributes
NEW QUESTION 2:
Which Layer 3 VPN attribute installs customer routes in the VRF?
A. RD
B. RT
C. extended-community
D. MPLS label
Correct Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 3:
Refer to the Exhibit.

The access-lists are configured on the network device. There is a server behind the network device. User are trying to access the server securely however they are not able to access it. What changes would you recommend to the above configuration?
A. Permit tcp port 465
B. Permit tcp port 3389
C. Permit tcp port 443
D. Permit tcp any any
Correct Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 4:
A CoPP policy is applied for receiving SSH traffic from the WAN interface on a Cisco ISR4321 router. However, the SSH response from the router is abnormal and stuck during the high link utilization. The problem is identified as SSH traffic does not match in the ACL. Which action resolves the issue?
A. Rate-limit SSH traffic to ensure dedicated bandwidth.
B. Apply CoPP on the control plane interface.
C. Increase the IP precedence value of SSH traffic to 6.
D. Apply CoPP on the WAN interface inbound direction.
Correct Answer: B
The problem is that “SSH traffic does not match in the ACL” and “CoPP policy is applied for receiving SSH traffic from the WAN interface” so we should apply CoPP on the control plane interface instead.
NEW QUESTION 5:
Refer to the exhibit. After applying IPsec, the engineer observed that the DMVPN tunnel went down, and both spoke-to-spoke and hub were not established. Which two actions resolve the issue? (Choose two.)
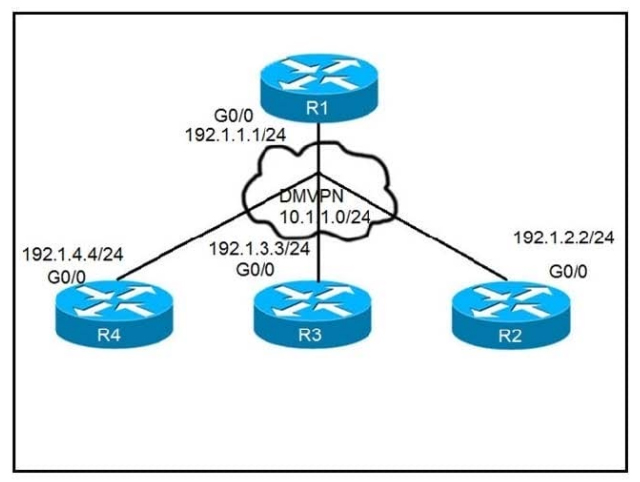

A. Change the mode from mode tunnel to mode transport on R3.
B. Remove the crypto isakmp key cisco address 10.1.1.1 on R2 and R3.
C. Configure the crypto isakmp key cisco address 192.1.1.1 on R2 and R3.
D. Configure the crypto isakmp key cisco address 0.0.0.0 on R2 and R3.
E. Change the mode from mode transport to mode tunnel on R2.
Correct Answer: BD
NEW QUESTION 6:
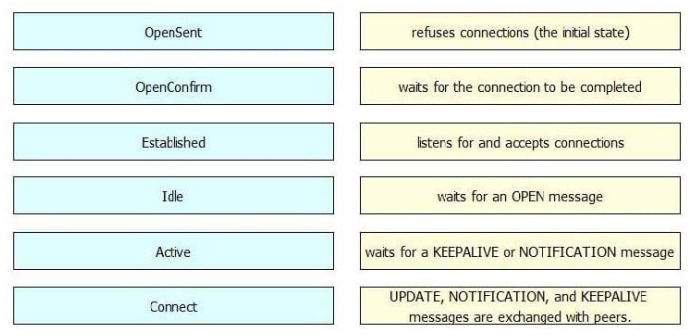
DRAG DROP
Drag and drop the BGP states from the left to the matching definitions on the right.
Select and Place:
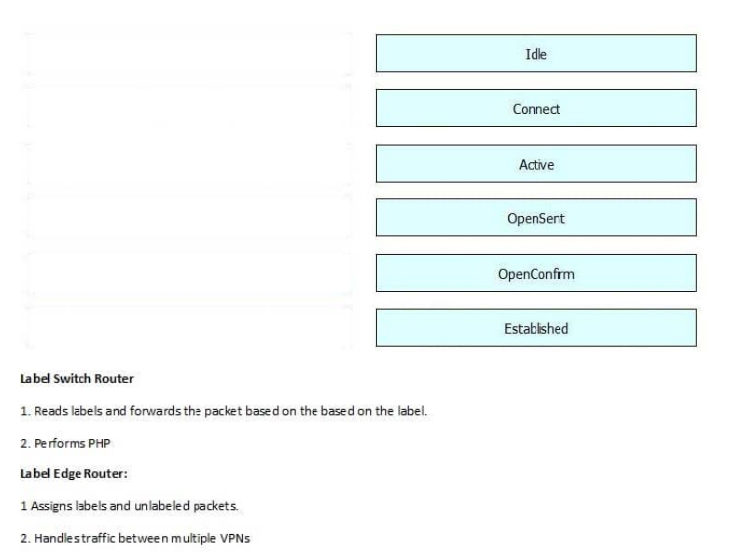
Correct Answer:
NEW QUESTION 7:
Refer to the exhibit
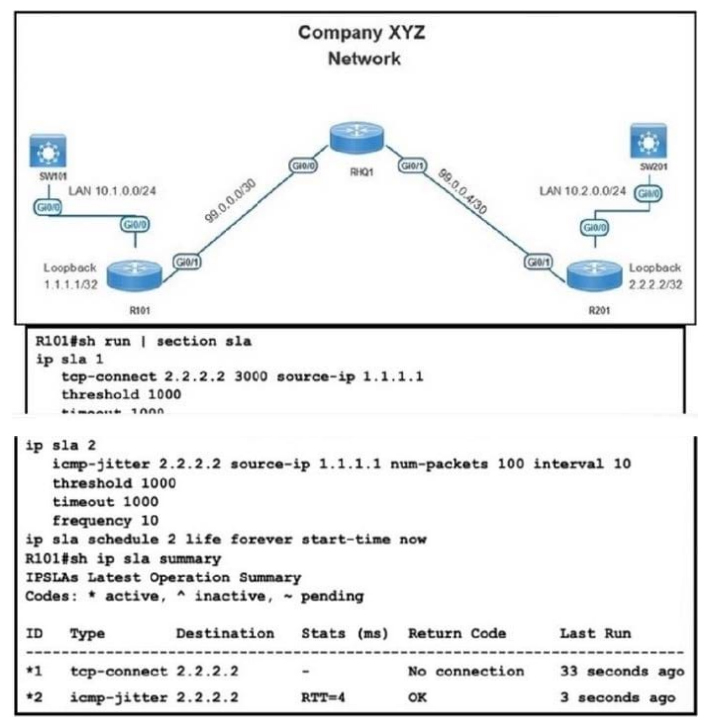
While troubleshooting an issue on the network, an engineer noticed that a TCP Connect operation failed on port 3000 between R101 and R201.
Which command must be configured on R201 to respond to the R101 IP SLA configurations with a control connection on UDP port 1967?
A. ip sla responder udp-echo IP address 1.1.1.1 port 1967
B. ip sla responder tcp-connect IP address 1.1.1.1 port 3000
C. ip sla responder tcp-connect IP address 2.2.2.2 port 3001
D. ip sla responder
Correct Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 8:
Refer to the exhibit.
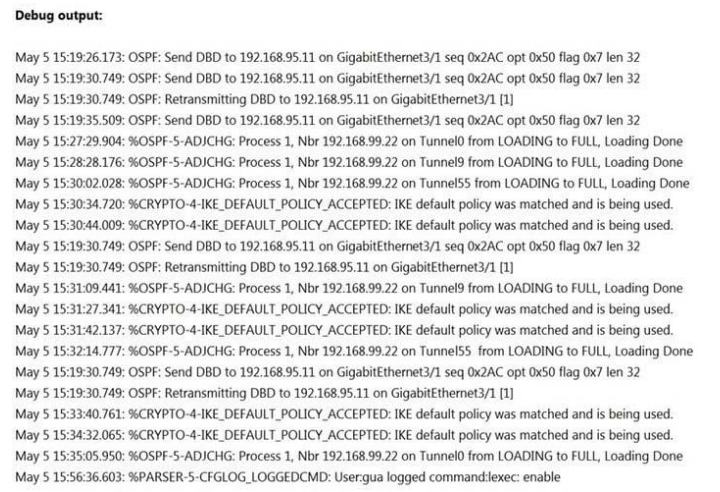
A network administrator is troubleshooting the OSPF adjacency issue by going through the console logs in the router, but due to an overwhelming log messages stream, it is impossible to capture the problem.
Which two commands reduce console log messages to relevant OSPF neighbor problem details so that the issue can be resolved? (Choose two.)
A. debug condition ospf neighbor
B. debug condition interface
C. debug condition session-id ADJCHG
D. debug condition all
E. debug condition ip
Correct Answer: BC
sw#debug condition os % Unrecognized command sw#debug condition session-id Session Number for debug filtering
NEW QUESTION 9:
You instructed your assistant to configure load balancing on a router. The router currently has two routes to network A. One route has a cost of 15, and the other has a cost of 30.
What command should the assistant execute to instruct the router to treat the two routes as equal without including any other routes in the load balancing?
A. routerA(config)# variance 2
B. routerA(config-router)# variance 2
C. routerA(config)# variance 3
D. routerA(config-router)# variance 3
Correct Answer: B
The correct command to instruct the router to treat the two routes as equal is variance 2. It must be entered in EIGRP configuration mode, as evidenced by the routerA(config-router)# prompt. The number that comes after the command is called the multiplier. A multiplier of two tells the router that any route that is within twice the metric of the best route will be considered equal to the best route.
The default setting for variance is one, which indicates that the routes must be equal to be considered for load balancing. An additional requirement of load balancing is that the alternate route\’s feasible distance must not be higher than the advertised distance of the route, which could indicate a routing loop.
The assistant should not execute the variance 2 commands at the routerA(config)# prompt, which is in global configuration mode. The variance command must be entered in EIGRP configuration mode at the routerA (config-router)# prompt.
The assistant should not use the variance 3 command in either mode because that would direct the router that any route within three times the cost of the best route (in this scenario, a cost of 45) would be considered equal to the cost of the best route. The scenario requires that two routes be load-balanced. Because one route has a cost of 15 and the other has a cost of twice 15 (30), the variance multiplier must be two.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify EIGRP load balancing
References:
Cisco > Home > Support > Technology Support > IP > IP Routing > Design > Design Technotes > How Does Unequal
Cost Path Load Balancing (Variance) Work in IGRP and EIGRP? Cisco > Support > Technology Support > IP > IP Routing
Design > Design Technotes > Route Selection in Cisco Routers > Document ID: 8651
NEW QUESTION 10:
Refer to the exhibit.
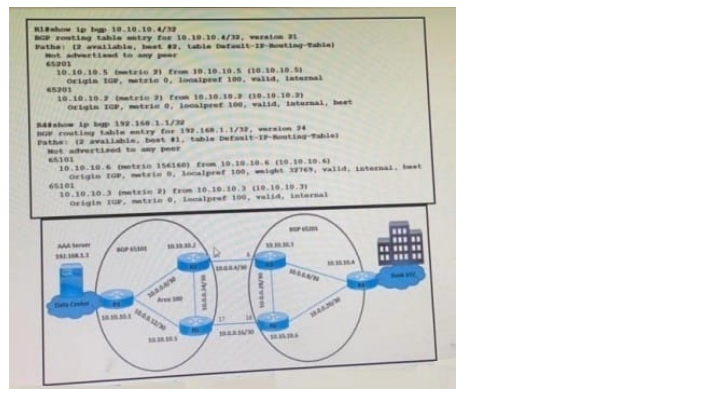
A customer reports that user traffic of bank XYZ to the AAA server is not using the primary path via the R3-R2 link.
The network team observes:
No fiber is cut on links R2 and R3.
As101 and AS 201 routers established BGP peering.
Which configuration resolves the issue?

A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Correct Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 11:
Refer to the exhibit.
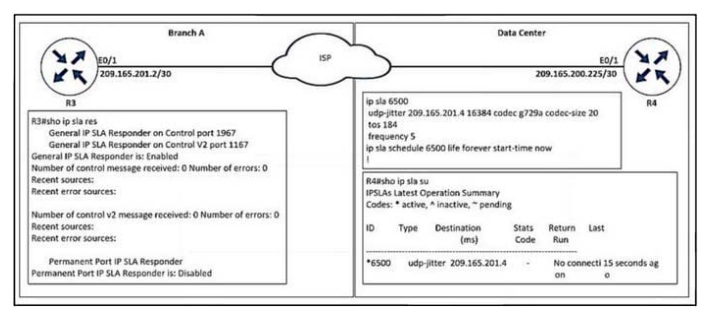
Which action resolves the IP SLA for the UDP jitter problem between R4 and R3 Ethernet 0/1 IP addresses?
A. Delete and configure the IP SLA 6500 commands with the R3 e0/1 IP address.
B. Configure the ip sla 6500 command with R3 e0/1 IP address.
C. Configure the IP sla responder command with R4 E0/1 IP address.
D. Delete and configure the IP SLA responder command with the R4 E0/1 IP address.
Correct Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 12:
Refer to the exhibit.
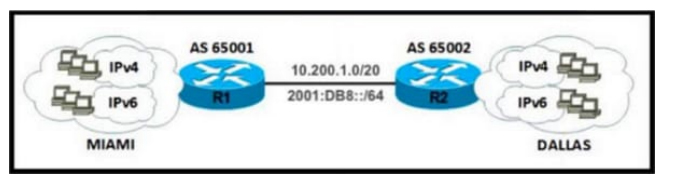
A network engineer configured routers R1 and R2 with MP-BGP. The engineer noticed that the routers cannot exchange any IPv6 routes; however, the IPv4 neighbor relationship is working fine. Which configuration must the engineer apply to router R2 to exchange IPv6 routes?


A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Correct Answer: B
… Follow us! We will continue to update the latest exam materials.
New 300-410 ENARSI Exam Materials Online Download:
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1iUDFe03BNZcVuNnBYCyHWNNJDCm8CIMy/view?usp=sharing

What’s the best comparison? View actual 2023 and 2024 exam materials.
[Updated 2023]: Online Download Section leads4pass 300-410 dumps: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1qJwgww9AdC5xAY_tJat4ED7cU9A_wNHt/
[Updated 2023] Online practice part leads4pass 300-410 dumps
| Type | Number of exam questions | Exam name | Exam code |
| Free | 15 | Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI) | 300-410 |
Question 1:
Refer to the exhibit. Users in the branch network of 2001:db8:0:4::/64 report that they cannot access the Internet. Which command is issued in IPv6 router EIGRP 100 configuration mode to solve this issue?

A. Issue the eigrp stub command on R1.
B. Issue the no eigrp stub command on R1.
C. Issue the eigrp stub command on R2.
D. Issue the no eigrp stub command on R2.
Correct Answer: B
Question 2:
Refer to the exhibit. Which configuration configures a policy on R1 to forward any traffic that is sourced from the 192.168.130.0/24 network to R2?

A. access-list 1 permit 192.168.130.0 0.0.0.255 ! interface Gi0/2 ip policy route-map test ! route-map test permit 10 match ip address 1 set ip next-hop 172.20.20.2
B. access-list 1 permit 192.168.130.0 0.0.0.255 ! interface Gi0/1 ip policy route-map test ! route-map test permit 10 match ip address 1 set ip next-hop 172.20.40.2
C. access-list 1 permit 192.168.130.0 0.0.0.255 ! interface Gi0/2 ip policy route-map test ! r oute-map test permit 10 match ip address 1 set ip next-hop 172.20.20.1
D. access-list 1 permit 192.168.130.0 0.0.0.255 ! interface Gi0/1 ip policy route-map test ! route-map test permit 10 match ip address 1 set ip next-hop 172.20.40.1
E. access-list 1 permit 192.168.130.0 0.0.0.255 ! interface Gi0/1 ip policy route-map test ! route-map test permit 10 match ip address 1 set ip next-hop 172.20.20.1
Correct Answer: D
Question 3:
R2 has a locally originated prefix 192.168.130.0/24 and has these configurations: What is the result when the route-map OUT command is applied toward an eBGP neighbor R1 (1.1.1.1) by using the neighbor 1.1.1.1 route-map OUT out command?

A. R1 sees 192.168.130.0/24 as two AS hops away instead of one AS hop away.
B. R1 does not accept any routes other than 192.168.130.0/24
C. R1 does not forward traffic that is destined for 192.168.30.0/24
D. Network 192.168.130.0/24 is not allowed in the R1 table
Correct Answer: A
Question 4:
Which method changes the forwarding decision that a router makes without first changing the routing table or influencing the IP data plane?
A. nonbroadcast multiaccess
B. packet switching
C. policy-based routing
D. forwarding information base
Correct Answer: C
Question 5:
Refer to the exhibit. The output of the traceroute from R5 shows a loop in the network. Which configuration prevents this loop?


A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Correct Answer: A
Question 6:
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer configures a static route on a router, but when the engineer checks the route to the destination, a different next hop is chosen. What is the reason for this?

A. Dynamic routing protocols always have priority over static routes.
B. The metric of the OSPF route is lower than the metric of the static route.
C. The configured AD for the static route is higher than the AD of OSPF.
D. The syntax of the static route is not valid, so the route is not considered.
Correct Answer: C
The AD of the static route is manually configured to 130 which is higher than the AD of the OSPF router which is 110.
Question 7:
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer is trying to generate a summary route in OSPF for network 10.0.0.0/8, but the summary route does not show up in the routing table. Why is the summary route missing?

A. The summary-address command is used only for summarizing prefixes between areas.
B. The summary route is visible only in the OSPF database, not in the routing table.
C. There is no route for a subnet inside 10.0.0.0/8, so the summary route is not generated.
D. The summary route is not visible on this router, but it is visible on other OSPF routers in the same area.
Correct Answer: C
The summary address is only used to create aggregate addresses for OSPF at an autonomous system boundary.
It means this command should only be used on the ASBR when you are trying to summarize externally redistributed routes from another protocol domain or you have an NSSA area. But a requirement to create a summarized route is:
The ASBR compares the summary route\’s range of addresses with all routes redistributed into OSPF on that ASBR to find any subordinate subnets (subnets that sit inside the summary route range). If at least one subordinate subnet exists,
the ASBR advertises the summary route.
Question 8:
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer is trying to block the route to 192.168.2.2 from the routing table by using the configuration that is shown. The route is still present in the routing table as an OSPF route. Which action blocks the route?

A. Use an extended access list instead of a standard access list.
B. Change sequence 10 in the route-map command from permit to deny.
C. Use a prefix list instead of an access list in the route map.
D. Add this statement to the route map: route-map RM-OSPF-DL deny 20.
Correct Answer: B
Question 9:
What is a prerequisite for configuring BFD?
A. Jumbo frame support must be configured on the router that is using BFD.
B. All routers in the path between two BFD endpoints must have BFD enabled.
C. Cisco Express Forwarding must be enabled on all participating BFD endpoints.
D. To use BFD with BGP, the timer’s 3 9 commands must first be configured in the BGP routing process.
Correct Answer: C
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios/12_0s/feature/guide/fs_bfd.html#wp1043332
Question 10:
Refer to the exhibit. R2 is a route reflector, and R1 and R3 are route reflector clients. The route reflector learns the route to 172.16.25.0/24 from R1, but it does not advertise to R3. What is the reason the route is not advertised?

A. R2 does not have a route to the next hop, so R2 does not advertise the prefix to other clients.
B. Route reflector setup requires full IBGP mesh between the routers.
C. In route reflector setup, only classful prefixes are advertised to other clients.
D. In route reflector setups, prefixes are not advertised from one client to another.
Correct Answer: A
Question 11:

Refer to the exhibit. An engineer is trying to redistribute OSPF to BGP, but not all of the routes are redistributed. What is the reason for this issue?
A. By default, only internal routes and external type 1 routes are redistributed into BGP
B. Only classful networks are redistributed from OSPF to BGP
C. BGP convergence is slow, so the route will eventually be present in the BGP table
D. By default, only internal OSPF routes are redistributed into BGP
Correct Answer: D
If you configure the redistribution of OSPF into BGP without keywords, only OSPF intra-area and inter-area routes are redistributed into BGP, by default.
You can redistribute both internal and external (type-1 and type-2) OSPF routes via this command:
Router(config-router)#redistribute ospf 1 match internal external 1 external 2
Question 12:
Refer to the exhibit.

In which circumstance does the BGP neighbor remain in the idle condition?
A. if prefixes are not received from the BGP peer
B. if prefixes reach the maximum limit
C. if a prefix list is applied in the inbound direction
D. if prefixes exceed the maximum limit
Correct Answer: D
Question 13:
Which attribute eliminates LFAs that belong to protected paths in situations where links in a network are connected through a common fiber?
A. Shared Risk Link Group (SRLG)-disjoint
B. linecard-disjoint
C. lowest-repair-path-metric
D. interface-disjoint
Correct Answer: A
LFA Tie-Breaking Rules
When there are multiple candidate LFAs for a given primary path, EIGRP uses a tie-breaking rule to select one LFA per primary path per prefix. A tie-breaking rule considers LFAs that satisfy certain conditions or have certain attributes. EIGRP uses the following four attributes to implement tie-breaking rules:
–
Interface-disjoint—Eliminates LFAs that share the outgoing interface with the protected path.
–
Linecard-disjoint—Eliminates LFAs that share the line card with the protected path.
–
Lowest-repair-path-metric—Eliminates LFAs whose metric to the protected prefix is high. Multiple LFAs with the same lowest path metric may remain in the routing table after this tie-breaker is applied.
–
Shared Risk Link Group (SRLG)-disjoint—Eliminates LFAs that belong to any of the protected path SRLGs. SRLGs refer to situations where links in a network share a common fiber (or a common physical attribute). If one link fails, other links in the group may also fail. Therefore, links in a group share risks.
Question 14:
Refer to the exhibit.

An engineer is troubleshooting BGP on a device but discovers that the clock on the device does not correspond to the time stamp of the log entries. Which action ensures consistency between the two times?
A. Configure the service timestamps log uptime command in global configuration mode.
B. Configure the logging clock synchronize command in global configuration mode.
C. Configure the service timestamps log datetime localtime command in global configuration mode.
D. Make sure that the clock on the device is synchronized with an NTP server.
Correct Answer: C
The Time zone needs to be changed. default it UTC Central European Time (CET)
Question 15:
Refer to the exhibit. What is the result of applying this configuration?

A. The router can form BGP neighborships with any other device.
B. The router cannot form BGP neighborships with any other device.
C. The router cannot form BGP neighborships with any device that is matched by the access list named “BGP”.
D. The router can form BGP neighborships with any device that is matched by the access list named “BGP”.
Correct Answer: C
After bgp session is UP. I configured the CoPP to drop 10.3.3.3 bgp traffic (R3). R3 bgp traffic that matched the ACL 100 is dropped and the state is in IDLE ——————————————– access-list 100 permit tcp host 10.3.3.3 any eq bgp access-list 100 permit tcp host 10.3.3.3 eq bgp any! class-map match-all class-bgp match access-group 100! policy-map policy-bgp class class-bgp drop! control-plane service-policy input policy-bgp! The 10.3.3.3 neighbor goes to IDLE
Get new materials for free!! Although they are only part of the leads4pass 300-410 dumps!
Now, use PDF or VCE to practice leads4pass 300-410 dumps: https://www.leads4pass.com/300-410.html (877 Q&A), assisting you to pass the Cisco 300-410 ENARSI certification exam 100% successfully.